How to Create an AWS S3 Bucket Using Terraform
Introduction
Terraform is an open-source IaC tool by HashiCorp. Infrastructure as Code (IaC) allows developers and DevOps engineers to automate cloud resource provisioning in a reliable and repeatable way. Lets you define cloud infrastructure declaratively and manage it efficiently.
In this blog, we’ll walk through how to:
- Launch an EC2 instance and install Terraform
- Write a Terraform configuration to create an S3 bucket
- Use AWS best practices (no ACLs, tagging, and private access by default)
Prerequisites
- AWS Account with IAM user credentials (Access Key + Secret Key).
- EC2 Instance (Ubuntu/Debian preferred).
- AWS CLI configured (
aws configurewith your keys). - Terraform installed on EC2 (we’ll cover this step).
Step 1: Install Terraform on the EC2 Instance
Connect to your EC2 instance via SSH:
| ssh -i your-key.pem ubuntu@your-ec2-public-ip |
Run the following commands to install Terraform:
| sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y wget unzip wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.9.8/terraform_1.9.8_linux_amd64.zip unzip terraform_1.9.8_linux_amd64.zip sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/ terraform -v |
- You should see the Terraform version displayed.
- Terminal output showing
terraform -vwith version1.9.8.
Step 2: Create Terraform Configuration
Create a new directory for your Terraform files:
| mkdir terraform cd terraform |
Create a file called main.tf:
| terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = “hashicorp/aws” version = “6.9.0” } } } provider “aws” { region = “ap-south-1” } resource “aws_s3_bucket” “my_bucket” { bucket = “my-test-bucket-name-6789-202508201030” # Must be globally unique tags = { Name = “TerraformS3Bucket” Environment = “Dev” } } |
Step 3: Initialize Terraform
| terraform init |
This downloads the AWS provider plugin.
Step 4: Validate and Apply
Check if your configuration is valid:
| terraform validate |
Preview changes before applying:
| terraform plan |
Apply the configuration:
| terraform apply |
Type yes when prompted. Terraform will generate a unique S3 bucket name
Screenshot attached:
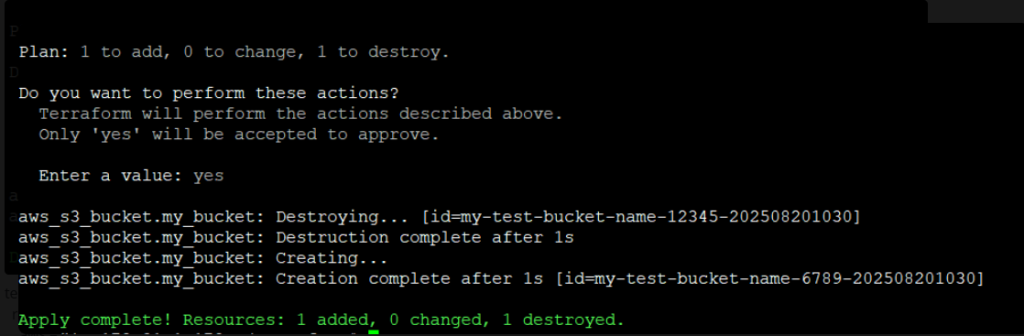
Step 5: Verify in AWS Console
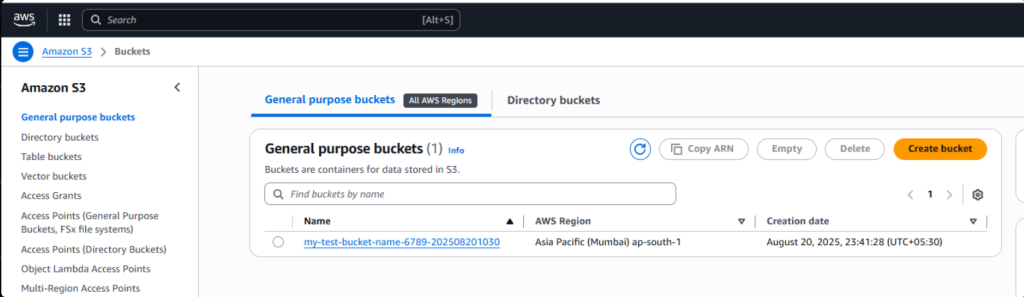
- Go to the AWS S3 Console
- Search for your newly created bucket. We can see the S3 bucket that we created using Terraform.
Conclusion
Using Terraform on an EC2 instance makes it easy to define and manage AWS resources. In this guide, we created an S3 bucket. This approach ensures your infrastructure is secure, repeatable, and scalable. With just a few commands, you’ve automated S3 bucket creation — and this same process can scale to VPCs, EC2 instances, databases, and more.
