Joining Tables with JOIN Clauses in Database
Joining Tables with JOIN Clauses in Database
Date posted: 02/05/2019
Join clause:
The SQL Join clause is used to combine records from two or more tables in a database.
A JOIN means for combining fields from two tables by using
common values to each.
Different types of joins
- INNER JOIN – selects records that have matching values in both tables.
- LEFT JOIN− selects all rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table.
- RIGHT JOIN– selects all rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
Pre-requesties
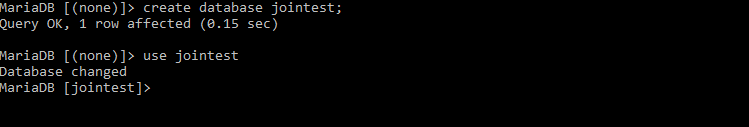
we have to create database and table. Firstly, create database and name it as ‘join test’. Then use the database.
Similarly, create a tables ‘s_table1 ‘ with column name ‘s_id’ and ‘s_name’.

Similarly in the vein, create a tables ‘s_table2 ‘ with column name ‘s_id’ and ‘s_city’.

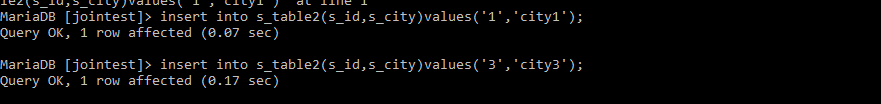
‘s_table1 ‘ and ‘s_table2’ data:

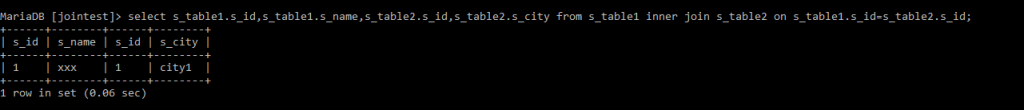
INNER JOIN :
MariaDB [jointest]> select s_table1.s_id,s_table1.s_name,s_table2.s_id,s_table2.s_city from s_table1 inner join s_table2 on s_table1.s_id=s_table2.s_id;
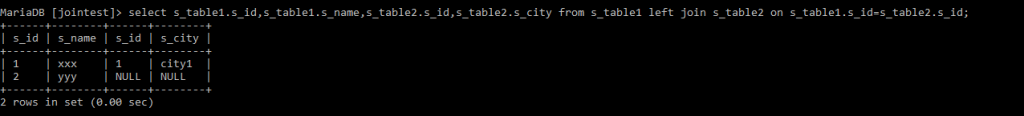
LEFT JOIN
MariaDB [jointest]> select s_table1.s_id,s_table1.s_name,s_table2.s_id,s_table2.s_city from s_table1 left join s_table2 on s_table1.s_id=s_table2.s_id;
RIGHT JOIN
MariaDB [jointest]> select s_table1.s_id,s_table1.s_name,s_table2.s_id,s_table2.s_city from s_table1 right join s_table2 on s_table1.s_id=s_table2.s_id;

Thanks for using pheonix solutions.
You find this tutorial helpful? Share with your friends to keep it alive
